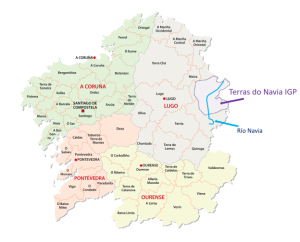
As published in the February 15 (2023) edition of the Official Journal of the European Union, the EU has announced the approval of a new IGP wine region for Spain: Terras do Navia, located in Galicia. The traditional term for Spain’s IGP regions is Vino de la Tierra (VdlT), and as such, this new appellation may show on wine labels as Vino de la Tierra—Terras do Navia.
As published in the February 15 (2023) edition of the Official Journal of the European Union, the EU has announced the approval of a new IGP wine region for Spain: Terras do Navia, located in Galicia. The traditional term for Spain’s IGP regions is Vino de la Tierra (VdlT), and as such, this new appellation may show on wine labels as Vino de la Tierra—Terras do Navia.
The new IGP will cover an area surrounding the Río Navia (Navia River) close to the eastern edge of the province of Lugo. This is a moderately high-elevation area located within the western reaches of the Cantabrian Mountains (Cordillera Cantábrica). The surrounding mountains reach elevations up to 1,000 meters/f3,280 feet above sea level, while the majority of the vineyards are situated at 200 to 500 meters/656 to 1,640 feet asl. Most of the vines are planted on south and south-west facing slopes, which provide some protection from the maritime influences coming in from the coast (45 km/29 miles away). The climate is described as mostly Mediterranean but includes transitional microclimates exhibiting Maritime and Continental influences as well. The finest vineyards are those with south/southwest aspect and abundant sunshine (due to elevation).
The Terras do Navia IGP is approved for white wines (blanco) and red wines (tinto). The regulations governing these wines include the following:
- Blanco/White Wines:
- Approved varieties: Albariño, Caíño Blanco, Godello, Loureira, Torrontés, and Treixadura
- Minimum alcohol by volume: 11.5%
- Flavor profile, as per the pliego de condiciones: fresh and smooth, highly aromatic (fruity and floral), well-balanced with crisp acidity
- Tinto/Red Wines:
- Approved varieties: Brancellao, Bruñal, Caíño Tinto, Loureiro Tinto, Mencía, and/or Merenzao (Trousseau)
- Minimum alcohol by volume: 10%
- Flavor profile, as per the pliego de condiciones: fresh and smooth, aromas of ripe red fruit (strawberry, blackberry, cherry, and cranberry), moderate alcohol, moderate tannin; oak aging is advisable but not required
The Terras do Navia IGP is scheduled to enter into force by March 8, 2023. According to the latest list of geographical indications from the Spanish Ministry of Agriculture (updated in September of 2022), Terras do Navia will be the 43rd VdlT/IGP wine region in Spain. Terras do Navia represents the fifth VdlT area in Galicia—joining Barbanza e Iria, Betanzos, Ribeiras do Morrazo, and Valle del Miño-Ourense. As well-versed wine students already know, Galicia is also home to five Denominaciones de Origen (DOs) for wine: Monterrei, Ribeira Sacra, Ribeiro, Rías Baixas, and Valdeorras.
References/for more information:
- Application-Terras do Navia PGI-English
- Extract from the EU Register-Terras do Navia
- Pliego de Condiciones-Terras-do-Navia-Spanish
- https://www.cope.es/emisoras/galicia/lugo-provincia/lugo/mundo-agrario-en-lugo/noticias/nace-igp-vitinicola-terras-navia-20230215_2552929
- https://www.agrodigital.com/2022/10/25/la-ixp-terras-do-navia-solicita-el-reconocimiento-comunitario/
Post authored by Jane A. Nickles…your blog administrator: jnickles@societyofwineeducators.org