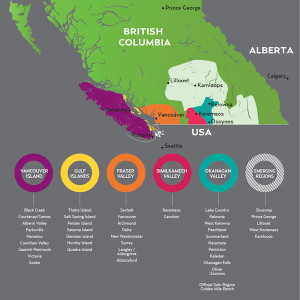
Shuswap, Lillooet, Thompson Valley, and Kootenays…what do these four things have in common?
They are newly-approved geographical indications (GIs) for quality wine in British Columbia (Canada)! These four areas are all located just north of Washington State, inland from British Columbia’s coastal wine-producing regions—Vancouver Island, the Gulf Islands, and Fraser Valley—and somewhat to the north and east of the well-established Okanagan Valley and Similkameen Valley GIs.
Here’s a quick look at these four new regions:
Shuswap: Located in and around the shores of Shuswap Lake, the Shuswap GI is located just to the north of the Okanagan Valley in the mountains of the Coast Range (on the map, it’s located to the west of the city of Kamloops). At 50°59´N latitude, it is among the northern-most fine wine producing regions in the world. This area has been producing wine since the late 1990s, focusing on cool-climate varietals. There are currently about 85 acres of commercial vineyards and ten licensed wineries in the area, including Larch Hills Winery, Baccarta Ridge Winery, Ovino Winery, and the irresistibly-named Edge of the Earth Vineyards. The name Shuswap is derived from the Shuswap (Secwepemc) First Nations people.
Lillooet: The Lillooet GI is located to the north of both the Fraser Valley and the Okanagan Valley, at just above 50°N in latitude. Despite this fact, however, the area can experience very warm days during the summer—as a matter of fact, this area sometimes clocks some of Canada’s highest temperatures during the summer days. The area is also dry, some years receiving as little as 13 inches (33 m) of rain. This is all due to the rain shadow and impressive gorges of the Coast Mountain Range. However, the high temperatures of the summer days drop steeply down at night, making this area slightly cooler overall than surrounding regions—considered the overall average temperature (hot days + cool nights). Commercial viticulture arrived in Lillooet in 2004, and there are currently 54 acres of vines, as well as one winery, Fort Berens Estate Winery in the area. The name is derived from the St’at’imc First Nations People, also known as the Lillooet Nation.
Thompson Valley: The Thompson Valley GI is located near the town of Kamloops—in and around the spot where the North Thompson River flows into the South Thompson River. Similar to the climate of Lillooet, the area is affected by the rain shadow of the Coast Mountains, and experiences some hot temperatures during the summer (accompanied by a nice diurnal swing). The area’s first commercial winery, Harper’s Trail Estate Winery, opened in 2012. The area boasts over 95 acres of vineyards and a handful of wineries—including Sagewood Winery and Privato Winery. The Thompson River and the Thompson Valley are named for David Thompson, an explorer and surveyor who mapped the entire length of the Columbia River in the early 1800s.
Kootenays: The Kootenays area, located along the southern border of British Columbia just to the east of the Okanagan Valley, is sometimes referred to as the “first shores” due to the fact that, according to geologists, the area was the original west coast of North America. The region has long been planted with apple orchards and is known for its many cider, cyser, and mead producers. Grapes have also been planted here, among the rivers, lakes, and waterfalls, since 1995. The Kootenays GI currently has just over 68 acres planted to vines and a handful of wineries, including Ballie-Grohman Estate Winery, Wynnwood Cellars, and Skimmerhorn Winery. The area is named for the Kootenay River (and Kootenay Mountain), which are themselves named for the Kutenai First Nations people.
For those of you studying for advanced wine certifications, it might be noted that that British Columba now has a total of 12 GIs (10 GIs and two sub-GIs). The entire list (as of October 1, 2018) is as follows:
- British Columbia GI
- Fraser Valley GI
- Gulf Islands GI
- Kootenays GI
- Lillooet GI
- Okanagan Valley GI (contains two sub-appellations: Golden Mile Bench GI and Okanagan Falls GI)
- Shuswap GI
- Similkameen Valley GI
- Thomson Valley GI
- Vancouver Island GI
*Keep those flashcards handy, however. There are two more sub-GIs in the pipeline: Skaha Bench and Naramata Bench (both of which are pending sub-GIs of the Okanagan Valley).
References/for more information:
- Wines of British Columbia: http://winebc.com/
- BC Wine Authority: http://www.bcvqa.ca/
- British Columbia – Wines of Marked Quality Regulation – July 27, 2018
- Media Kit Wines of British Columbia