News flash from Spain: After previous approval by the Government of Andalucía (Junta de Andalucía), the Spanish Ministry of Agriculture (Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación) has published a new-and-revised Pliego de Condiciones for the Jerez-Xérès-Sherry DO. While these changes represent some significant updates to the time-honored production requirements of Sherry, they do not encompass all of the changes that were expected; other updates are still awaiting approval.
The changes to the Jerez-Xérès-Sherry DO include the following:
New grapes allowed: In addition to the traditional three varieties (Palomino, Pedro Ximénez, and Moscatel de Alejandría), the following grape varieties are now approved for use in Sherry: Beba, Perruno, and Vigiriega. These grapes were common to the region prior to phylloxera.
Introducing…Fino Viejo: Fino Viejo is a new category of wine, representing biologically aged wines with an average of seven years of solera aging; these wines must show substantial oxidative character.
Minimum sugar levels have been lowered: The minimum required sugar content has been lowered (from 5 grams per liter) to 4 g/L.
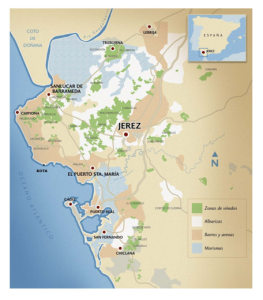
Official sub-zones have been listed: Sub-zones, referred to as Pagos or Unidades Geográficas Menores de la Zona Delimitada (minor geographic units of the delimited zone) have been defined. There are over 100 pagos currently so designated. Click here for a list and a map of the pagos, via the website of the consejo regulador.
Note: As with all such updates, this change will need to wind its way through EU authorization; however, as the government of Spain has granted their approval, the changes are considered to be in force. If the EU fails to approve the amendment, the regulation will be rescinded.
References/for more information:
Post authored by Jane A. Nickles…your blog administrator: jnickles@societyofwineeducators.org