“Fortified Wine Day” in my professional wine studies class is one of my favorite classes to teach. The incredible array of colors, aromas, and flavors offered by fortified wines amazes the students, and the rich histories of Port, Madeira, and Sherry are full of tales ripe for the telling.
“Fortified Wine Day” in my professional wine studies class is one of my favorite classes to teach. The incredible array of colors, aromas, and flavors offered by fortified wines amazes the students, and the rich histories of Port, Madeira, and Sherry are full of tales ripe for the telling.
It’s a favorite day for the students as well, although that could be due to the 20% alcohol content of some of the wines.
Yesterday, after tasting Ruby Port, one of my students asked, “dude, what would happen if you just added brandy to grape juice…would it be like extreme fortification?” At least that’s what I think he said.
It’s a good question, albeit in need of some editing. What if we asked it question a bit more properly, as in: “What would happen if a winemaker added grape spirits to wine must, before it even begins to ferment?”
The answer would be “Vin de Liqueur!” Vin de Liqueur is a unique type of fortified wine that is fortified just before or just after fermentation begins, creating a strong, sweet liquid. Vin de Liqueur is very close in style to Vin Doux Naturel; the main difference being that Vin Doux Naturel is allowed to ferment until the residual sugar reaches around 10%.
Vins de Liqueur are made in many places throughout Europe. They are often referred to as “Mistelle” or “Mistela,” and the style has been copied in the new world as well. The Italians make good use of the technique, producing a blend of unfermented grape juice and brandy called “Sifone” that is often used, in turn, as a sweetening agent in Marsala.
 The most famous French Vin de Liqueur is Pineau des Charentes, made in the départements of Charente and Charente-Maritime in Southwestern France. The region of origin is technically the same as the region of origin for Cognac. Pineau de Charentes is produced by combining Cognac with freshly pressed grape juice, in a ratio of approximately one part Cognac to three parts must. The Cognac must be at least one year old, and the mixture is aged for at least 18 months in oak.
The most famous French Vin de Liqueur is Pineau des Charentes, made in the départements of Charente and Charente-Maritime in Southwestern France. The region of origin is technically the same as the region of origin for Cognac. Pineau de Charentes is produced by combining Cognac with freshly pressed grape juice, in a ratio of approximately one part Cognac to three parts must. The Cognac must be at least one year old, and the mixture is aged for at least 18 months in oak.
Two older varieties are also made, including Vieux Pineau, which is at least 5 years old, and Tres Vieux Pineau, (“Very Old Pineau,” if my high school French hasn’t failed me), which is at least 10 years old. These older versions are rich, complex works of art as compared to the fruity, floral, and crisply acidic young version.
Many of the large Cognac houses make Pineau, and there are several small, artisan producers that focus on Pineau exclusively. The Cognac house of Normandin-Mercier makes several versions, including white, rosé and “Tres Vieux.” Almost 90% of the Pineau de Charentes that is produced is consumed locally, with another large percentage going to Belgium. However, it is available in the United States and seems to have been discovered by the “Craft Cocktail Movement,” so it should be easy to find…just ask your local celebrity mixologist.
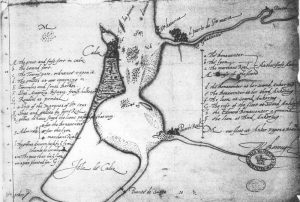
 As with many fortified wines, Pineau de Charentes has a good back story. This one tells of a wine and brandy making Monk who, in 1589, filled a barrel with freshly pressed grape must, not knowing that the barrel was already partially full of aging Cognac. Five years later, a bumper crop had him emptying out a series of barrels to use for new wine, and he discovered what he had done five years earlier. By this time, of course, his Cognac and grape juice “mistake” had evolved into a rich, thick, sweet liquid…and, as they say, the rest is history.
As with many fortified wines, Pineau de Charentes has a good back story. This one tells of a wine and brandy making Monk who, in 1589, filled a barrel with freshly pressed grape must, not knowing that the barrel was already partially full of aging Cognac. Five years later, a bumper crop had him emptying out a series of barrels to use for new wine, and he discovered what he had done five years earlier. By this time, of course, his Cognac and grape juice “mistake” had evolved into a rich, thick, sweet liquid…and, as they say, the rest is history.
Pineau de Charentes from Nonmandin-Mercier: http://cognacnm.fr/products-page/pineau-des-charentes/pineau-des-charentes-tres-vieux-blanc-75-cl-17-vol