The Maas River (known in France as the Meuse) runs for over 575 miles (925 km) from its source in France’s Grand Est Region. From there, it flows north through Belgium, then forms a portion of the border between Belgium and the Netherlands before turning slightly to the east and wandering a bit before joining the Hollands Diep and flowing into the North Sea.
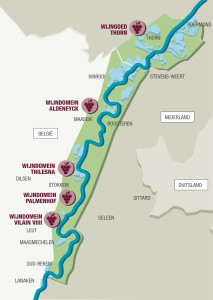
A portion of the area where the Maas forms the border between Belgium and the Netherlands (about 60 square miles) is known as the Maasvallei Limburg. Maasvallei Limburg has (believe it or not) recently been designated as a PDO wine region by the European Union. This is noteworthy for several reasons, including the area’s northerly location (between 50° and 51ºN) and the fact that this will be the first PDO wine region that crosses the border and includes area within two separate EU countries.
According to the EU petition, “Grapes for wine were cultivated in the abbeys along the Maas in the early Middle Ages. Historical texts refer to modest wine production within the abbey walls. A number of place names also refer to vineyards—including “Wingerd” (vine)—which indicate a history of wine cultivation in the area. Wine was one of the reasons that the convent of noble Benedictine nuns in Thorn acquired its status as an abbey-principality.”
In modern times, winemaking is fairly new to the area, and still somewhat obscure with just 10 producers on the Belgian side of the area (including Wijnomein Aldeneyck) and only one on the Dutch side (Wijngoed Thorn).
The Maasvallei Limburg PDO is approved for varietally-labeled red and white wines—however, according to the EU documentation, “blending is allowed, but something of an exception.” Grapes approved for the region include the following:
- Red Grapes: Acolon (a Blauer Lemberger X Dornfelder cross), Dornfelder, and Pinot Noir
- White Grapes: Auxerrois, Chardonnay, Gewürztraminer, Pinot Blanc, Pinot Gris, Riesling, and Siegerrebe (a Madeleine Angevine X Gewürztraminer cross)
Welcome to the world, Maasvallei Limburg PDO!
References/for more information:
- https://www.thedrinksbusiness.com/2017/11/netherlands-poised-to-gain-first-pdo-wine-region/
- http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32017D0822(01)
- https://www.expatica.com/nl/news/country-news/Lifestyle-wine-EU-Netherlands-Belgium_1560107.html
- http://www.wijndomein-aldeneyck.be/
- http://wijngoed-thorn.nl/nl/3/nieuws
- http://wijngoed-thorn.nl/site/home.php