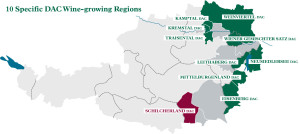
Note: As of March 3, 2019, the Schilcherland DAC has been rescinded and replaced by the Weststeiermark DAC. Schilcher rosé continues to be produced as a specialty of the Weststeiermark DAC.
We’re leaving this blog post—originally dated October 16, 2017—up and available in order to provide information on the late, great, historic Schilcherland DAC.
The Austrian wine region formerly known as Weststeiermark has been re-born as the Schilcherland DAC. This brings the total number of Districtus Austriae Controllatus regions (DACs) in Austria to ten. This change was announced via the website of the Austrian Wine Marketing Board today (October 16, 2017), and the changes will be reflected in the wines of the current vintage (2017) and moving forward.
The new DAC is approved for one type of wine only—rosé produced from 100% Blauer Wildbacher grapes. The grapes must be harvested by hand and the wine must be packaged in a glass bottle. There are two quality levels: Schilcherland “Klassik” DAC and Schilcherland DAC—which must specify a single vineyard (Ried) designation on the front label. Other requirements are noted below.
For Schilcherland Klassik DAC:
- The wine must be vinified dry (max. 3.0 g/l residual sugar)
- The wine should show no oak influence
- Alcohol content must range from a minimum of 11% to a maximum of 12% abv
- The flavor must be refreshing and fruit-forward, and should show aromas of strawberry, red currant and raspberry
Schilcherland DAC:
- The wine must be labeled with a specific vineyard (Ried) designation
- Minimum alcohol content of 12% abv
- The wine must be vinified dry (max. 4.0 g/l residual sugar)
- The wine should also be refreshing and fruit-forward and with no oak influence; but it is expected to have a deal more flavor intensity then the Klassik versions.
We’ll post more information as it becomes available, but for now—Welcome to the world, Schilcherland DAC!
References/for more information: