Today we have a guest post from Jim Gerakaris, CWE. Jim gives us a preview of his upcoming presentation, “What you Probably Don’t Know about Paso Robles: It’s Even Cooler than You Think!” This session will be presented at the 46th Annual Conference of the Society of Wine Educators. The conference is scheduled for August 10-11 in Coachella Valley (Indian Wells, CA).

.
What you Probably don’t Know about Paso Robles- It’s Even Cooler than You Think!
The dangers of being type cast are both great and frustrating. Just like actors that get cast in the same types of roles after seeing some initial success, the region of Paso Robles has been viewed in the wine world as that place that makes reliably rustic, chewy Zins that could never possibly be viewed as complex, balanced wines. Most of the current wine literature only repeats this same narrative about Paso Robles, but a lot has been happening in this region that warrants a second look, especially over the last few decades.
Beginning with the growing of mission grapes for the production of sacramental wine at Mission San Miguel in 1797, and nearly a century later with zinfandel vineyards planted by Swiss/Italian immigrants in the 1880s to make their wine in a new land, Paso Roble’s reputation was for a big, rustic wines that are often typical of a warmer region.

.
This style of winemaking continued until the 1980s, when a few newcomers began to realize the potential of making quality wines from classic grape varieties like Cabernet, Syrah and other highly regarded varieties while also exploring some exciting white varieties, especially those from the Rhone Valley.
The growing conditions of Paso Robles are very different than most other California wine regions and initially, conditions like alkaline soils, and low rain levels posed challenges to defying the norms that had yielded those rustic wines. Eventually a collective knowledge began to emerge regarding where to plant vines, what kind of root stock (if any) to use and how to farm grapes with a focus on quality not quantity. This, along with the advancements in viticulture and winemaking technology seen in the last thirty years have brought about a revolution that has redefined the reputation of Paso Robles and its wines. To show how much things have changed, Zinfandel now only comprises about 6% of the total planted acreage of the region.

.
The knowledge that was gained over this time has changed how the growers and wineries in Paso Robles began to view the AVA and most felt that the larger AVA designation was too broad and did not describe the nuance and potential that Paso Robles has to offer. In 2007, an independent committee including scientists from Cal Poly San Luis Obispo, submitted a petition the TTB to establish 11 sub-AVAs within the larger Paso Robles AVA to better describe the region’s growing conditions. In 2014, after a thorough review of the massive amount of data presented by the committee, the petitions were approved and since then, the region has emerged in a new light.
While Paso Robles has had some great press in the last few years, mostly in periodicals and in newspapers, the established wine literature is still lagging beyond stating the 11 sub AVAs, and a wine educator still needs to dig though many sources to get a better feel for the region and its potential.
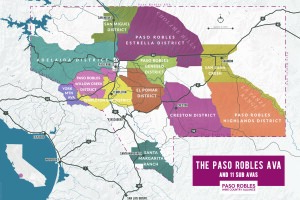
Map via: pasowine.com/paso-robles/ava/
For instance, here are a few things you may not know about the Paso Robles AVA:
- There are a wide range of climatic conditions from Zone II through Zone IV on the Winkler scale.
- Average precipitation varies widely from West to East, almost 40” to 10” respectively, affecting soil composition and other growing conditions.
- The soils are mostly calcareous and alkaline, typically 7.0 – 7.5 pH and above with about 30 distinct soil series.
- There are 600,000 acres in the greater Paso Robles AVA (42 miles east to west and 35 miles north to south), with 40,000 acres that are planted to grapes, just slightly less than the Napa Valley.
- Like Napa, the most planted grape variety is Cabernet Sauvignon (about 50% of total acreage planted).
- There is a diverse planting of varieties in the region including rarities like Aglianico, Vidiano, Picpoul Blanc and Clairette Blanche as well as Sauvignon Blanc, Riesling, Syrah, Tempranillo, petite Sirah, Viognier, grenache blanc and Roussanne to name just a few.
To learn and see more about the dynamic and developing region of Paso Robles, join Jim Gerakaris, CWE in an exploration of the unique combination of soils, climate and culture that has brought Paso Robles into prominence while tasting a variety of wines that is bound to surprise you. Jim’s session is scheduled for Wednesday, August 10th at 4:45 pm as part the 46th Annual Conference of the Society of Wine Educators, to be held August 10-11 in Coachella Valley (Indian Wells, CA).
About the speaker: Jim Gerakaris is the Winery Sommelier and Wine Educator at JUSTIN Vineyards & Winery in Paso Robles, CA. He is a Certified Wine Educator since 2014 and a Certified Sommelier since 2010. Through an early introduction to Bordeaux and other European wines, Jim fed his passion for food and wine while traveling internationally during a previous career in technical sales in the semiconductor industry. In 2003 he jumped ship and entered the wine industry in various winery hospitality positions in the Paso Robles area and has been at JUSTIN Vineyards & Winery since 2008. Known for his ability to convey complex concepts regarding wine to both the novice and the pro in an entertaining and memorable way. Jim is a senior member of the hospitality management team with a focus on education, a part of the blending team for JUSTIN wines and a frequent winery representative for JUSTIN at dinners, conferences, and other events in the U.S. and abroad.
 The government of Turkey (the country) has officially changed the English name of the country to Türkiye (tur-key-YAY), the spelling and pronunciation used in the Turkish language. As of June (2022), the United Nations has approved the change and mapmakers everywhere are sure to follow suit.
The government of Turkey (the country) has officially changed the English name of the country to Türkiye (tur-key-YAY), the spelling and pronunciation used in the Turkish language. As of June (2022), the United Nations has approved the change and mapmakers everywhere are sure to follow suit.