In March of 2020, Spain’s Ministry of Agriculture approved a proposal to modify the Pliego de Condiciones for the DO Ribera del Duero. The new rules allow for the production of white wines based on the Albillo Mayor grape variety to be bottled under the Ribera del Duero DO, beginning with the 2020 vintage.
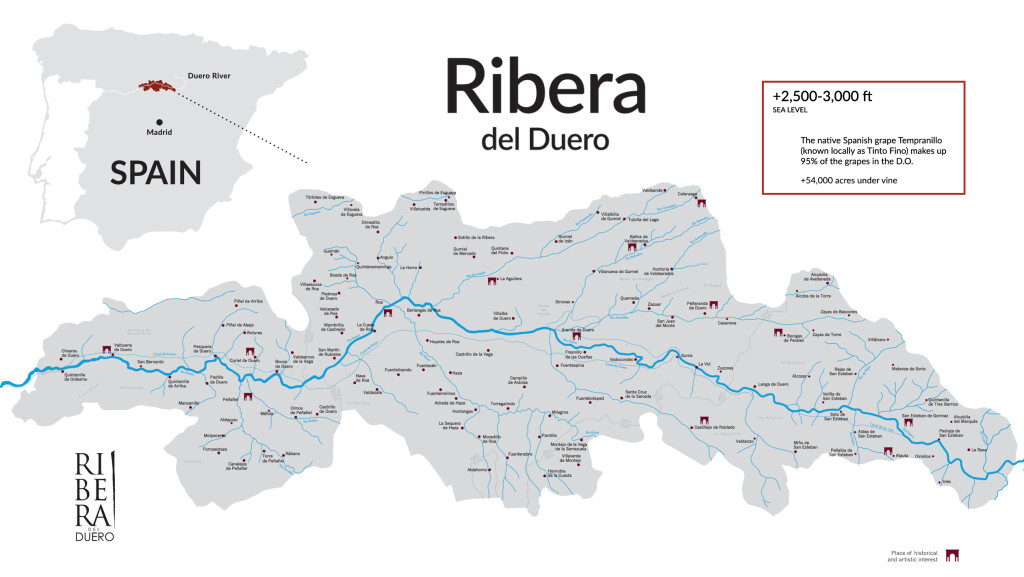
The Ribera del Duero DO—located in Castilla y León—was established in 1982 and quickly made a name for its flavorful red wines based on a minimum of 75% Tempranillo (often referred to here as Tinta del País or Tinto Fino). The red wines of the area always allowed for the inclusion of up to 5% Albillo Mayor—a white grape believed to be native to the area and grown in minute quantities but renowned for the rich aromatic notes and softening effect the it brought to the red wines of the region. Rosado is also produced in the area, often based on Garnacha with perhaps a bit of Merlot, Malbec, Cabernet Sauvignon or Albillo Mayor in the blend.
With the newly-published revisions in the rules, the Ribera del Duero DO is now producing white wines—known as Ribera Blanco—based on a minimum of 75% Albillo Mayor. The other white grapes allowed include Alarije (Pirulés) and Chasselas—provided they were planted prior to July 21, 1982.
Ribera Blanco may be produced via stainless steel fermentation as a light, fruity wine intended for early consumption. Such wines have been described as having delicate fruit flavors (green apple, lemon, pear) and lightly floral aromas.
Ribera Blanco may also be produced via oak fermentation and/or oak aging; and may be bottled under the typical aging designation for Spanish DOP wines (crianza, reserva, and gran reserva). Such wines are expected to show hints of gold or amber in the color and exhibit aromas of ripe pear, dried fruit, oak, smoke, beeswax, and vanilla.
The proposal to allow for the production of Ribera Blanco was originally published by El Boletín Oficial del Estado (BOE) of Spain on July 27, 2019. While the new DO regulations have been approved at the national level, they will still need to work their way through the EU approval process.
References/for more information:
- Pliego de Condiciones – DO Ribera del Duero – updated March 2020
- Press Kit – Ribera Blanco
- https://www.mapa.gob.es/es/alimentacion/temas/calidad-agroalimentaria/calidad-diferenciada/dop/vcprd/DOP_ribera-duero.aspx
Post authored by Jane A. Nickles…your blog administrator: jnickles@societyofwineeducators.org