On June 17, 2021, the TTB (Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau) of the United States approved two new American Viticultural Areas (AVAs): the White Bluffs AVA and the Burn of Columbia Valley AVA. When these new AVAs come into force—on July 19, 2021—the total number of AVAs in Washington State will be 18.
This article will focus on the Burn of Columbia Valley AVA. Click here for an article focusing on the While Bluffs AVA.
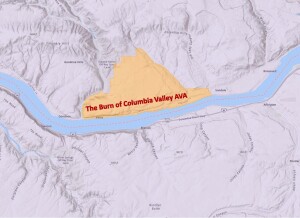
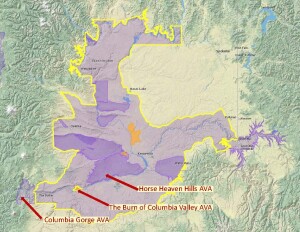
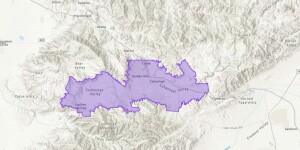
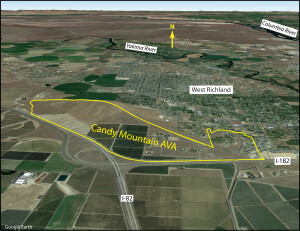
The Burn of Columbia Valley AVA (a sub-region of the Columbia Valley AVA) is located in the southwest corner of the Columbia Valley AVA, along a stretch of benchland on the north bank of the Columbia River. It is situated between the Horse Heaven Hills AVA (to its east) and the Columbia Gorge AVA (to its west). Its location along the Columbia River places it adjacent to the border between Washington State and Oregon—although it lies 100% in Washington State.
The petition to establish The Burn of Columbia Valley AVA (originally slated as “The Burn”) was submitted by Kevin Corliss of Ste. Michelle Wine Estates, Joan Davenport (Professor of Soil Sciences at Washington State University), and John Derrick of Mercer Ranches. According to the petition, the area’s distinguishing features include its topography, climate, and soils—as discussed below.
Topography: The area within the new AVA is situated on a moderately-elevated, gently sloping benchland above the Columbia River. The (generally) southeast-facing slope averages just over 7% grade.
Climate: The area is considered (overall) one of the warmer regions of the Columbia Valley. However, due to the persistent winds from the Columbia Gorge, the heat (as measured by “degree days”) accumulates much more slowly than in the surrounding areas. As a result, the growing season is extended—the grapes in this area are often among the last to be harvested in the state. This lengthy growing season allows for deep flavor development and excellent acid retention in the grapes.
Soils: The soils within the new AVA—dominated by Walla Walla silt loam—are, in many aspects, similar to those of the surrounding areas. However, the soils within The Burn contain a higher proportion of organic matter and lower levels of sand/sandy loam—and, as a result, the soils of The Burn have higher water- and nutrient-retention capacity. This means that the region has a lower need for supplemental irrigation, a lower need for the use of supplemental vine nutrients, and a reduced risk of winter vine injury as compared to the surrounding areas.
The triangle-shaped Burn of Columbia Valley AVA covers a total of 16,870 acres. Of these, approximately 1,500 acres/607 ha have been planted to vines. The region contains two commercial vineyards and no bonded wineries (as of 2021). This is a young growing area; while vines have been planted in the area since 2002, the majority of the vines have been planted since 2015. Cabernet Sauvignon is the leading variety, followed by Syrah, Malbec, Chardonnay, and Sangiovese.
About that name: there is no easy consensus on where the name—The Burn—originated, although there is plenty of evidence that it has been used in reference to the area for generations. The Burn might refer to a local legend that tells of early settlers who set fire to the benchland every fall in order to rejuvenate the native grasses and provide for their horses in the springtime. It could also be based on the Gaelic- German- and English-inspired use of the term burn (as in Bannockburn)—or born (as in Padderborn) or bourne (as in Melbourne)—to refer to a stream or a river.
Welcome to the world: The Burn of Columbia Valley AVA!
P.S. The TTB has also announced a new AVA in California—Palos Verdes Peninsula—to be effective on July 19, 2021. Click here for more details.
References/for more information:
- Federal Register-Establishment of the Burn of Columbia Valley AVA
- Petition to Establish The Burn of Columbia Valley AVA
- Washington State Wine (washingtonwine.org)
Post authored by Jane A. Nickles…your blog administrator: jnickles@societyofwineeducators.org