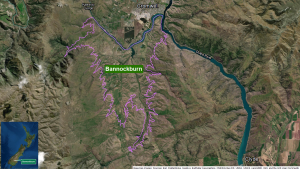
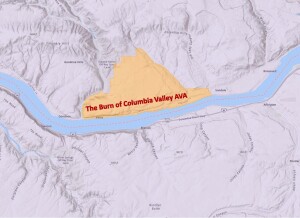
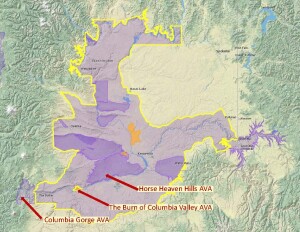
On February 1 (2022), the New Zealand Office of Intellectual Property registered Bannockburn as an official geographical indication (GI) for wine production. Bannockburn is now a registered sub-region of the Central Otago GI (as well as a GI in its own right).
In New Zealand—as is done in most of the world of wine beyond Europe—geographical indications do not assign restrictions as to grape varieties or wine styles grown and produced, but rather define just the physical boundaries of a region.
Here are some of the defining characteristics of the newly minted Bannockburn GI:
- The Bannockburn GI is located within the larger Cromwell Basin and defined by the Kawarau River and Lake Dunstan to the north and the high mountains of the Southern Alps—specifically the Cairnmuir and Carrick Ranges—to the east, south and west.
- The southern edge of the area is drawn along a contour measured at 400 meters/1,320 feet above sea level. From this line, the area slopes gently down to an elevation of 195 meters/650 feet, with generally north-facing slopes and terraces.
- Soil types include decomposed greywacke, schist, ancient lakebed sediment (alluvium), quartz (gravel), sand, and loess.
- The location—within the Cromwell Basin and surrounded by mountains—means that rainfall is low and the climate is classified as “truly continental.”’
- Bannockburn GI is the warmest part of Central Otago and further from the sea than most other points in New Zealand.
The leading grape varieties of the Bannockburn GI include Pinot Noir, Chardonnay, Pinot Gris, and Riesling. Minor plantings include Sauvignon Blanc, Chenin Blanc, Gewürztraminer, Pinot Blanc, and Grūner Veltliner. As of 2019, the area had total of 145 acres/350 hectares planted to commercial vines.
The first vinifera vines in the area were planted by John Olssen and Heather MacPherson in 1991. The term “Bannockburn” was first used on a wine label to indicate place-of-orign for grapes in 2009. At last count, there were six wineries operating in the area (and several others making wine from Bannockburn fruit). Current producers include Terra Sancta Winery, Felton Road Winery, Mount Difficulty, Carrick Winery, and Akura Winery.
Welcome to the world, Bannockburn GI!
Note: the Central Otago GI is considered to contain five other sub-regions. However, we have not (yet) found any evidence of an effort to declare these areas as geographical indications and as such, these other five sub-regions remain unofficial. For the record, they are: Gibbston; Cromwell, Lowburn and Pisa; Bendigo; Wanaka; and Alexandra.
References/for more information:
- https://www.iponz.govt.nz/about-ip/geographical-indications/register/bannockburn/
- Bannockburn GI-Application via the NZIPO
- Central Otago Wine Region | New Zealand Wine (nzwine.com) (includes a good map of Central Otago and sub-regions)
Post authored by Jane A. Nickles…your blog administrator: jnickles@societyofwineeducators.org